在根据Mybatis入门中有这么一段
String resource = "org/mybatis/example/mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);通过
mybatis-config.xml读取Mybatis相关配置,其中有一个<maperrs></mappers>节点则是对对应> 我们相关SQL映射文件
今天我们来研究Mybatis是如何加载一系列sql xml
映射器(mappers)
在 <mappers></mappers>节点当中可以使对应的具体的<mapper></mapper>也可以是一个包路径package如
<!-- 使用相对于类路径的资源引用 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/BlogMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/PostMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
<!-- 将包内的映射器接口实现全部注册为映射器 -->
<mappers>
<package name="org.mybatis.builder"/>
</mappers>
而对应的包路径则与java mapper文件一一对应 ,我们以包路径package为例相关路径


SqlSessionFactoryBuilder#build
在我们根据mybatis启动流程时会发现这么一段代码
//75
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
//xml解析
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
在 xmlConfigBuilder解析时会得到 Configuration配置类,所以我们进入解析看一下解析了啥东西
XMLConfigBuilder#parse
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
我们可以具体关注 parseConfiguration,至于 parser.evalNode("/configuration")这是对于的config.xml的configuration节点,这个就和DocumentBuilderFactory解析差不多
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
// issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
//插件
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
//对应的sql mapper xml
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
这个方法几乎是解析了configuration节点所有的信息
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
这里就是对应的mappers节点内容具体解析,可以看出一个就是package包节点和其他节点(取其他节点名应该无所谓,具体得有resource,url,class等属性)
所以我们继续看一看Configuration.addMappers(String packageName)方法
Configuration
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
mapperRegistry.addMappers(packageName);
}
- mapperRegistry 其内部就是一个map
MapperRegistry
/**
* Adds the mappers.
*
* @param packageName
* the package name
* @param superType
* the super type
* @since 3.2.2
*/
public void addMappers(String packageName, Class<?> superType) {
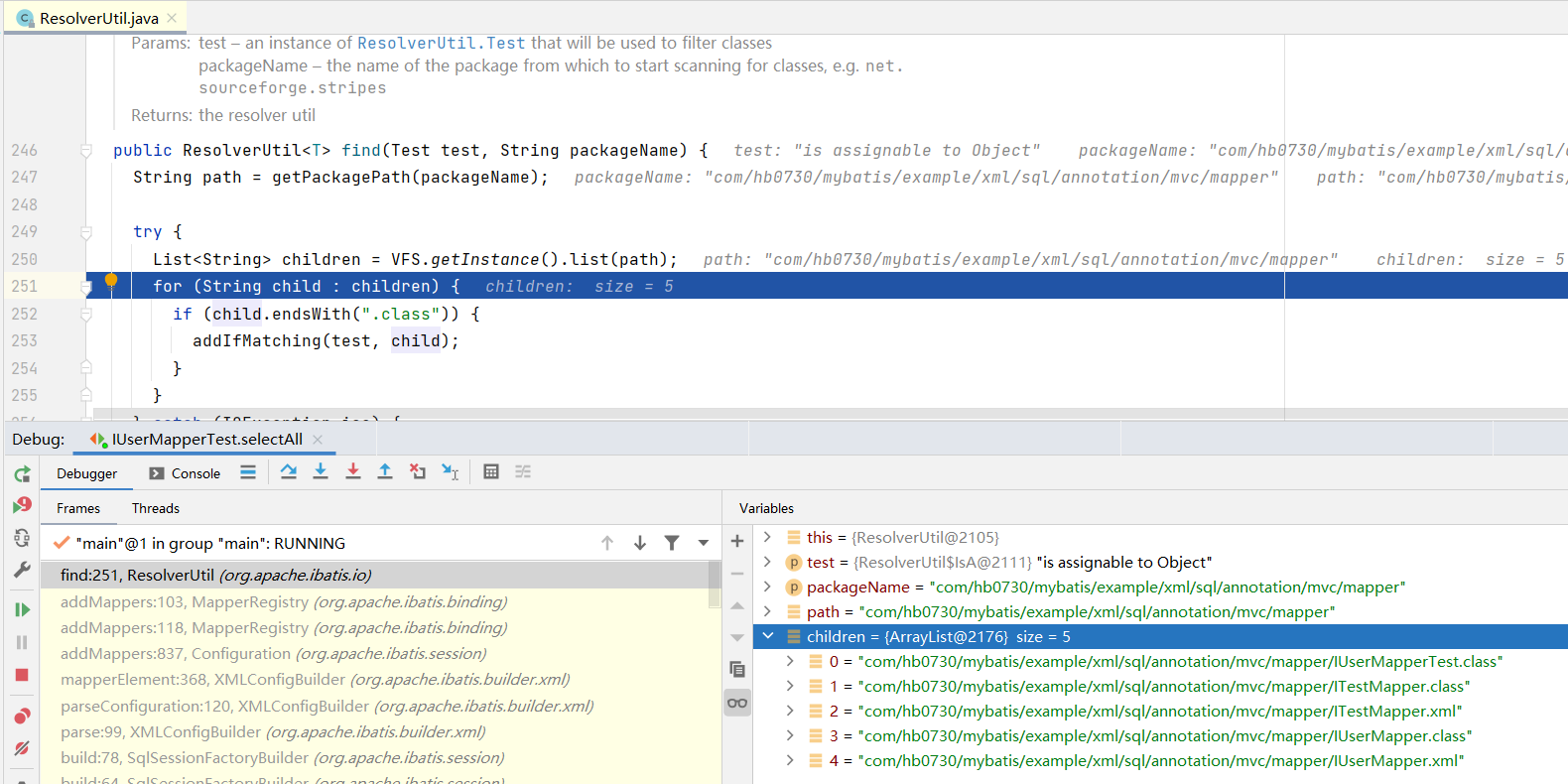
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for (Class<?> mapperClass : mapperSet) {
addMapper(mapperClass);
}
}
/**
* Adds the mappers.
*
* @param packageName
* the package name
* @since 3.2.2
*/
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
addMappers(packageName, Object.class);
}
其实我们可以看到这就是查询包下所有的xml
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
在这一步我们发现它还进行mapper解析,正如注释所说这很重要,我们瞧一瞧
MapperAnnotationBuilder
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
//1. 判断类是否加载过
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
//2. 加载对应的xml文件
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
//设置构建器助理的当前命名空间为type的包+类名
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
//3. 后面的都是解析接口中的注解
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
for (Method method : type.getMethods()) {
if (!canHaveStatement(method)) {
continue;
}
if (getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Select.class, SelectProvider.class).isPresent()
&& method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class) == null) {
parseResultMap(method);
}
try {
//构建MapperStatement对象,并添加到Mybatis全局配置信息中
parseStatement(method);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
在这里则是具体用来解析Mapper接口的xml文件和Mapper接口上的注解,感兴趣的可以具体研究研究